基础(Flexbox Fundamental)
- 弹性/伸缩盒子布局是一种简单而强大的 布局页面组件的方法,它规定了空间是如何分配的,内容是如何对齐的,元素在视觉上是如何排序的。
- 在元素声明
display: flex,此元素成为一个伸缩容器(flex container),在所提供的 空间内安排其子元素并控制它们的布局。伸缩容器的子元素变成伸缩项(flex items) - 一旦设置一个元素成为
伸缩容器,那么它只会flex其直接子代,而不会flex其进一步的后代。 - 在
flex容器中,flex项在主轴(main axis)上排成一行。
伸缩容器(Flex Container)
flex-direction: 控制主轴,flex项沿着主轴放置的。即指定如何在flex容器中放置flex 项。默认row,是主轴方向,也即是当前写入模式的方向(writing mode)1
2
3
4
5Value: row|row-reverse|column|column-reverse
Initial value: row
Applies to: flex container
Inherited: No
Animatable: No写入模式的方向(Writing Direction),由 CSS 中的
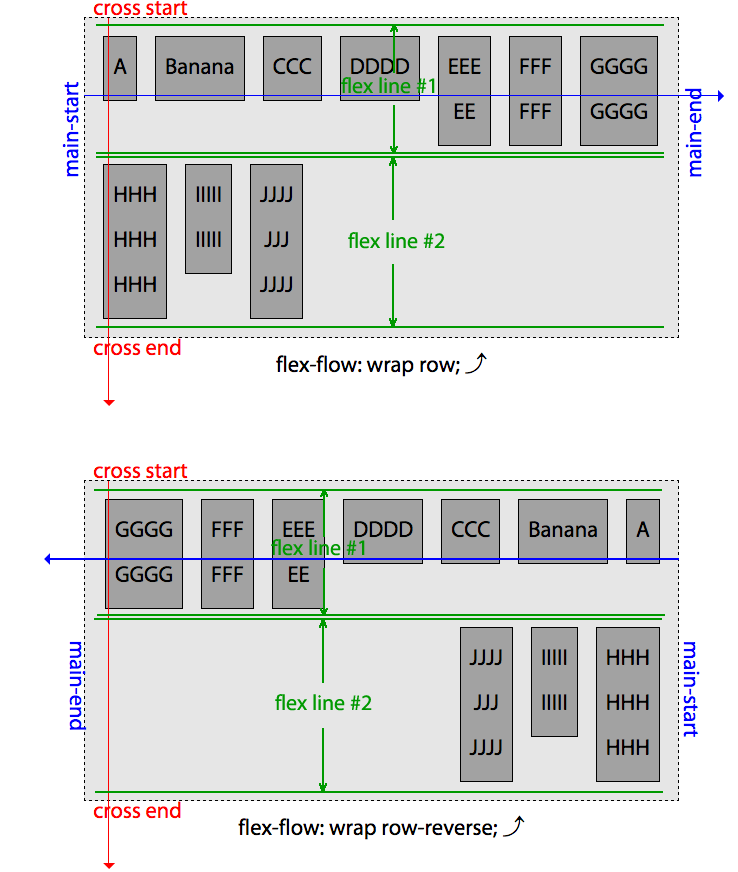
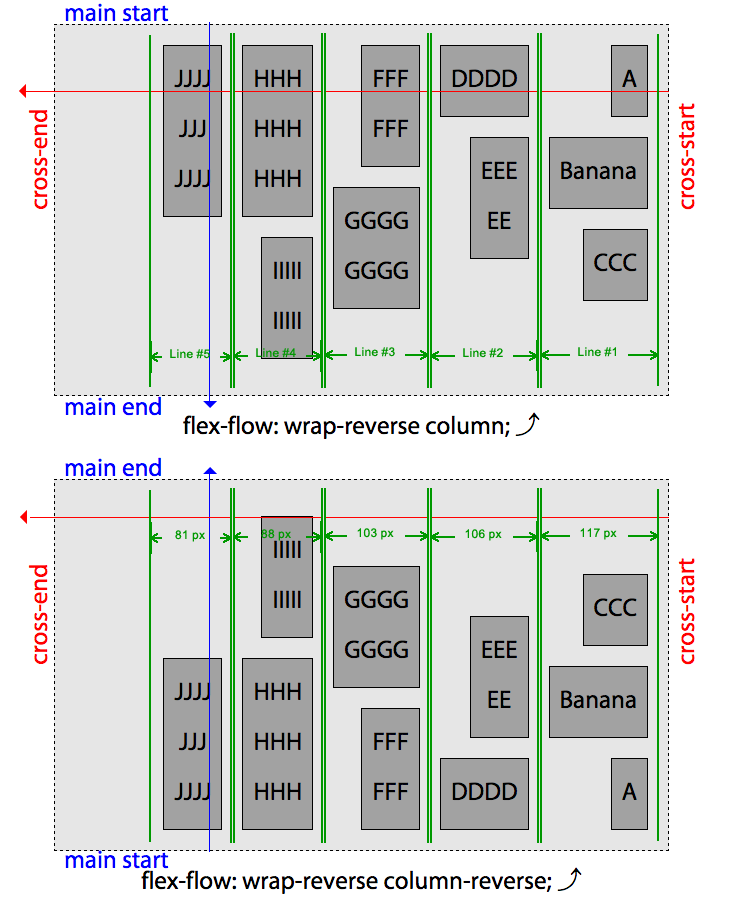
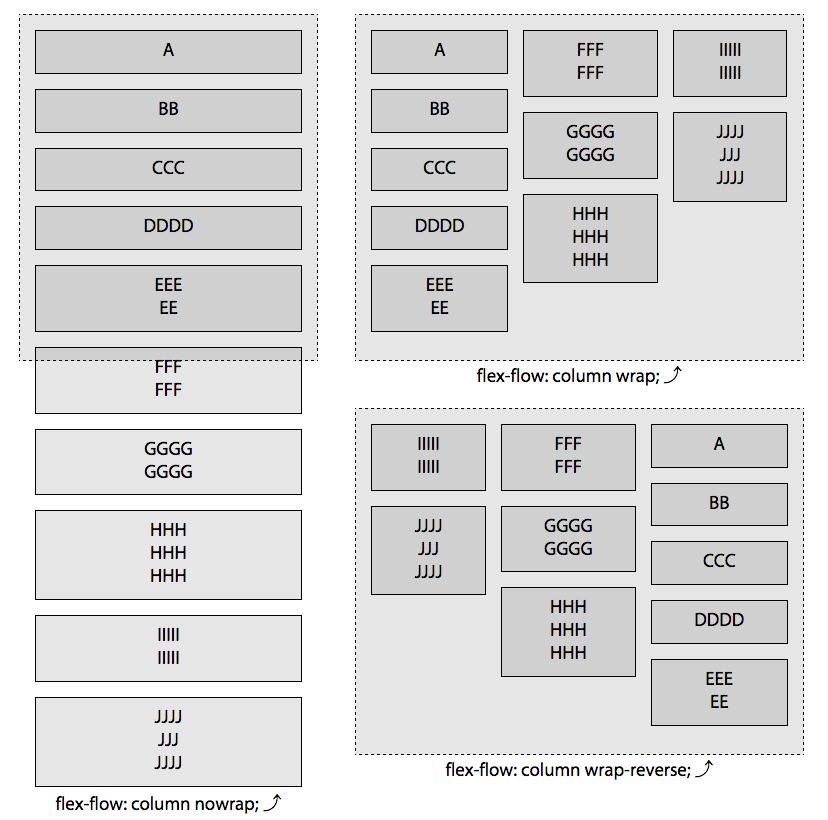
writing-mode,direction属性控制,或者由 HTML 中的dir属性控制。flex-wrap,控制flex 容器是否被限制为单行容器,或者在需要时允许成为多行容器。1
2
3
4
5Value: nowrap|wrap|wrap-reverse
Initial value; nowrap
Applies to: Flex contaier
Inherited: No
Animatable: Noflex-flow,flex-direction和flex-wrap的简写形式。 、1
2
3
4
5Vlaue: <flex-direction>||<flex-wrap>
Initial value: row nowrap
Applies to: Flex container
Inherited: No
Animatable: No理解弹性盒子中的轴(axes)
main axis:主轴,沿着 内容流动的轴,是flex 项流动的方向main size:内容腌主轴的总长度main start: 主轴上内容开始流动的一端main end: 内容流向的主轴的末端cross axis:沿着块堆叠的轴,是flex 项需要换行,放置flex 项目 行的方向
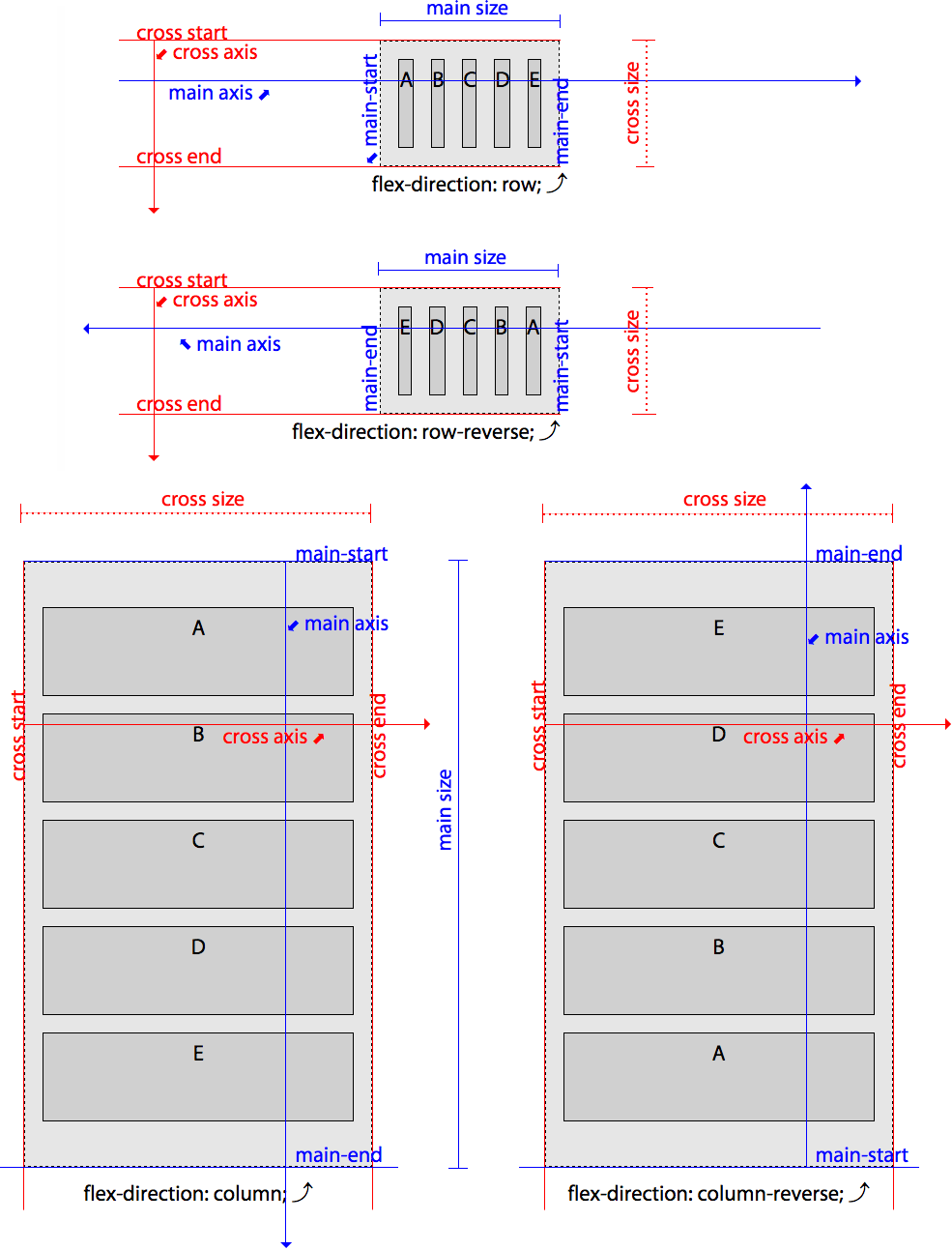
- Flex direction in LTR writing modes
| row | row-reverse | column | colum-reverse | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| main axis | left to right | right to left | top to bottom | bottom to top |
| main-start | left | right | top | bottom |
| main-end | right | left | bottom | top |
| main size | width | width | height | height |
| main dimension | horizontal | horizontal | vertical | vertical |
| cross axis | top to bottom | top to bottom | left to right | left to right |
| cross-start | top | top | left | left |
| cross-end | bottom | bottom | right | right |
| cross size | height | height | width | width |
| cross dimension | vertical | vertical | horizontal | horizontal |
排列 Flex 项(Arranging Flex Items)
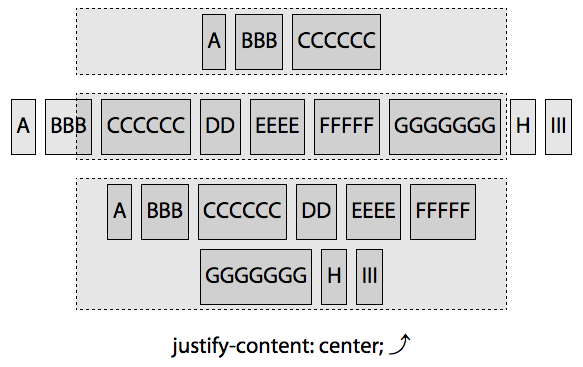
justify-content
justify-content属性定义了flex项在主轴flex 行上的如何对齐,一根轴线(flex line)上flex 项是如何分布的
1 | Value: flex-start|flex-end|center|space-between|space-around|space-evenly |
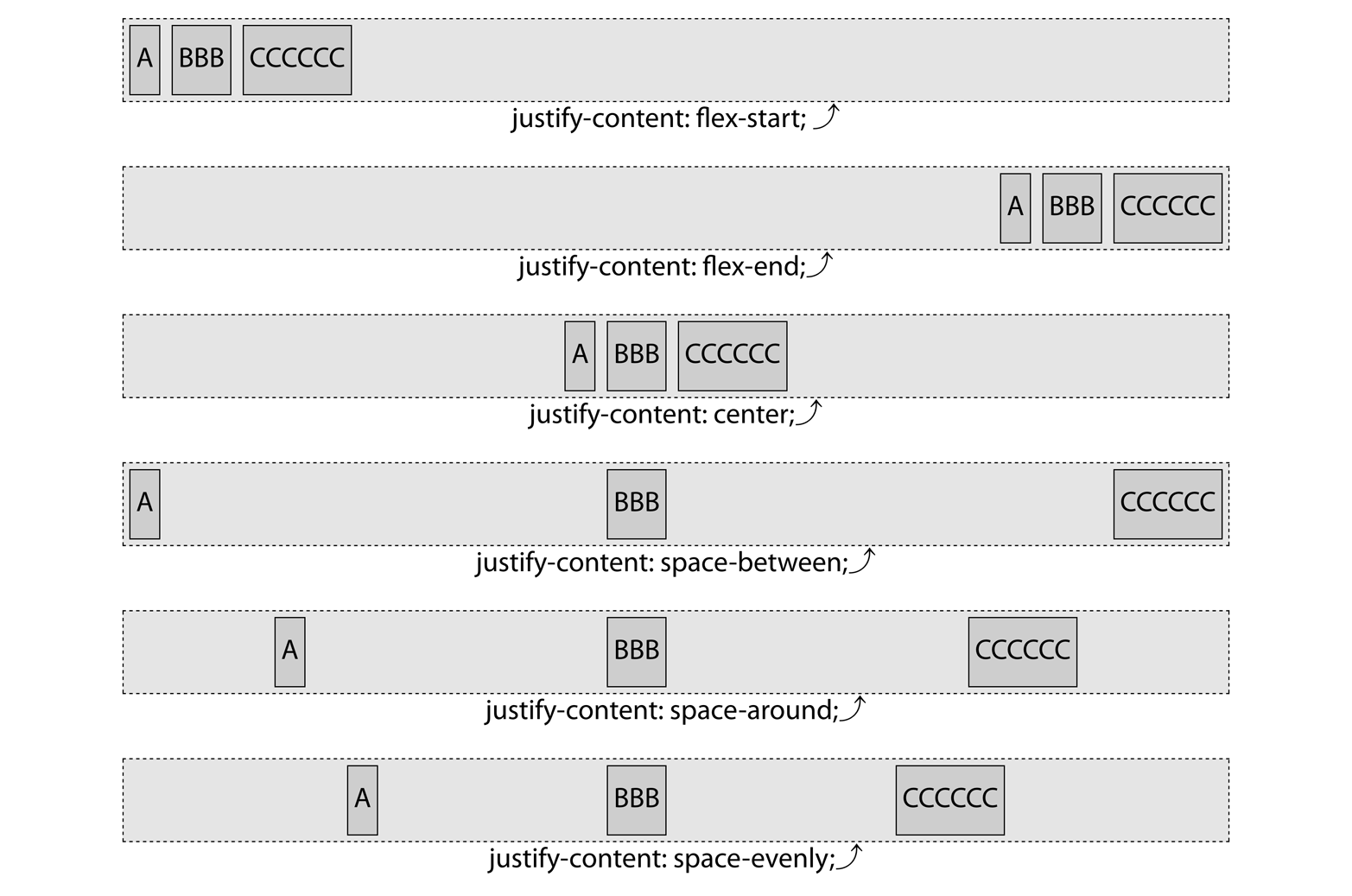
flex-start
flex-end
center
space-between
space-between将flex 行中的第一个flex 项与main-start对齐,最后一个flex 项与main-end对齐,然后在每个flex 项周围放置相同的空间,直到flex 行被填满。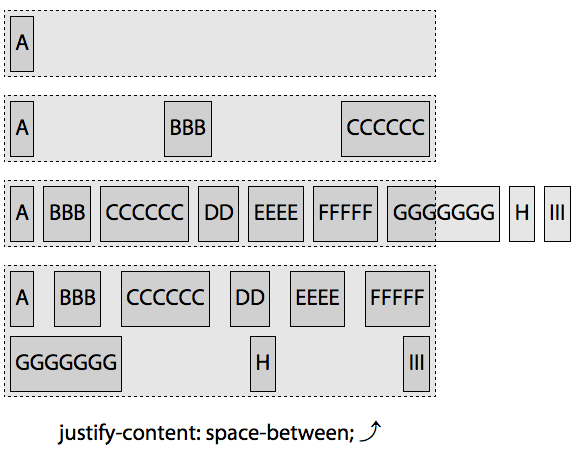
space-around
space-around均匀的把额外空间分配在每一flex 项周围,就好像每个flex 项周围都有大小相同的非折叠边距。因此,首项和第二项,尾项和倒数第二项之间的空间是其他中间项之间的 2 倍(项之间的空间是项与边框之间的 2 倍)。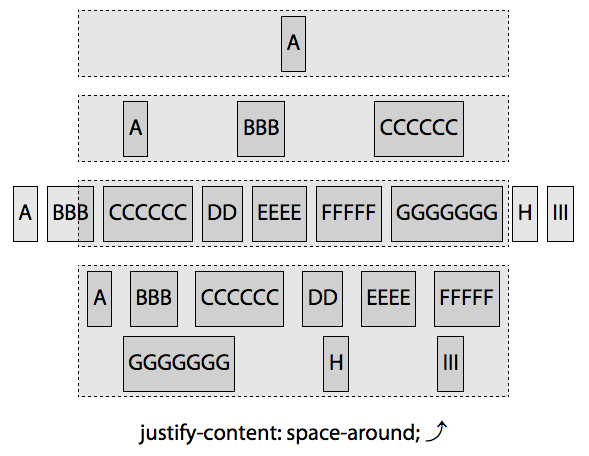
space-evenly
space-evenly,项与项之间,项与边框之间的空间相同。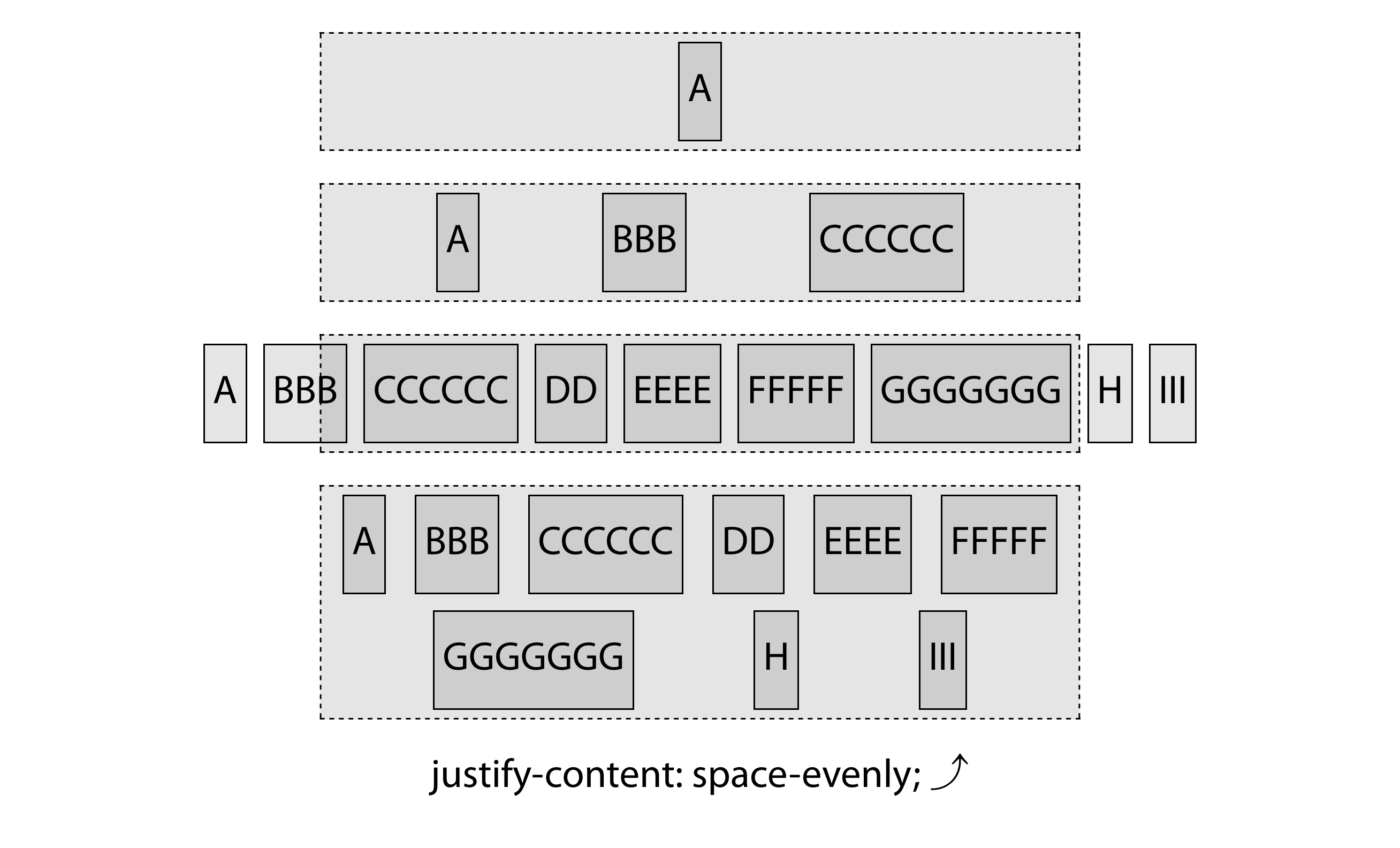
align-items
align-items属性定义每一个flex 行中flex项在交叉轴上如何对齐
1 | Value: flex-start|flex-end|center|baseline|stretch |

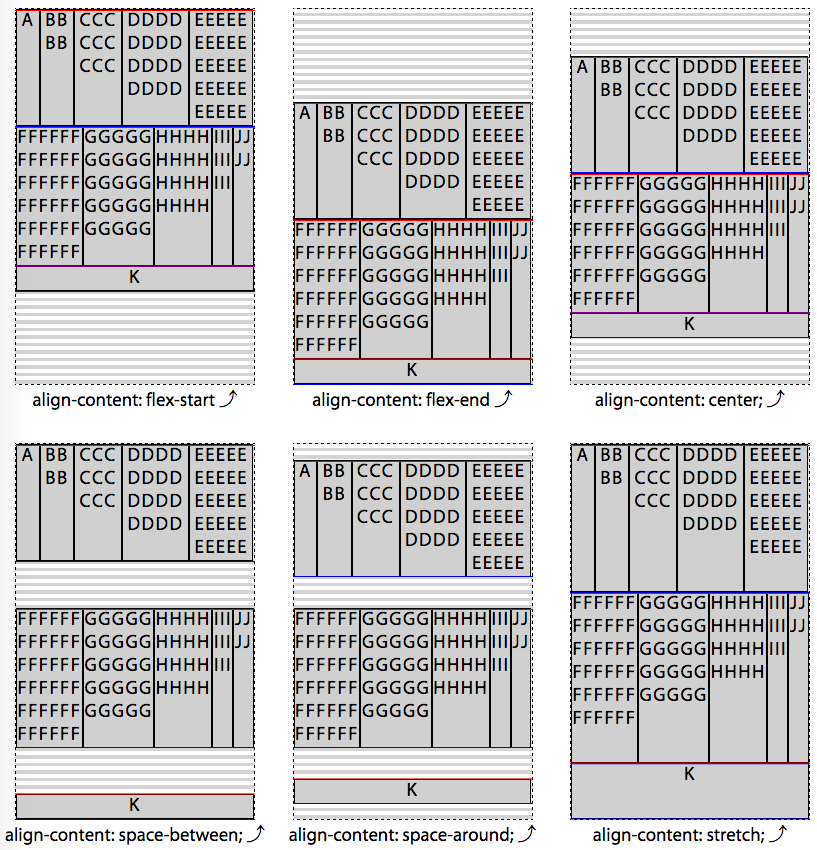
align-content
align-content属性定义了多个flex 行的如何沿着交叉轴对齐。
该属性仅适用于多flex 行的flex 容器
flex 项(Flex 项)
flex 容器的子元素被称为flex 项,包括子元素,子元素之间的非空文本节点,或者生成的内容。- 当
flex 容器包含文本节点时,且文本节点不是空的,它被包装在一个**匿名的flex 项**中,就像其它的flex 项的兄弟一样,并继承了flex 容器设置的所以 flex 属性。 - 空白的文本节点在
flex 容器中会被忽略。 flex 项的边距(margin)不会折叠。float,clear属性对flex 项没有影响,会被忽略。vertical-align对flex 项没有影响,除非它影响到flex 项内容文本的对齐。- 决定定位
flex 容器内的子元素,与其他任何决定定位元素一样,从文档流中移除。但是它会受到flex 容器的justify-content和align-self值的影响。
flex属性
虽然通过在flex 容器上设置属性,可以在一定程度上控制flex 项的对齐、顺序、伸缩性,但是也有几个属性(flex-grow,flex-shrink,flex-basis)可以应用到单个flex 项上,以实现更细粒度的控制
1 | Value: [<flex-grow><flex-shrink>?|| <flex-basis>]|none |
flex-basis是指每个flex 项的初始大小,可以通过指定grow和shrink因子为 0 来限定为特定的大小。
1 | .flexItem { |
以上 CSS,flex 项在主轴尺寸正好是 200px,其尺寸既不能增长也不能收缩。假若主轴是水平的,那么宽度值(50%)将被忽略。并且这种覆盖发生在 CSS 层叠之外,甚至不能通过添加!important来再覆盖掉
flex-grow
flex-grow不能是负值,可使用小数。它决定了当flex 容器有额外空间被分配时,**flex 项相对于其它felx 项**的增长幅度。- 额外空间根据增长因子的不同值按比例分配给具有非零正增长因子的子元素。
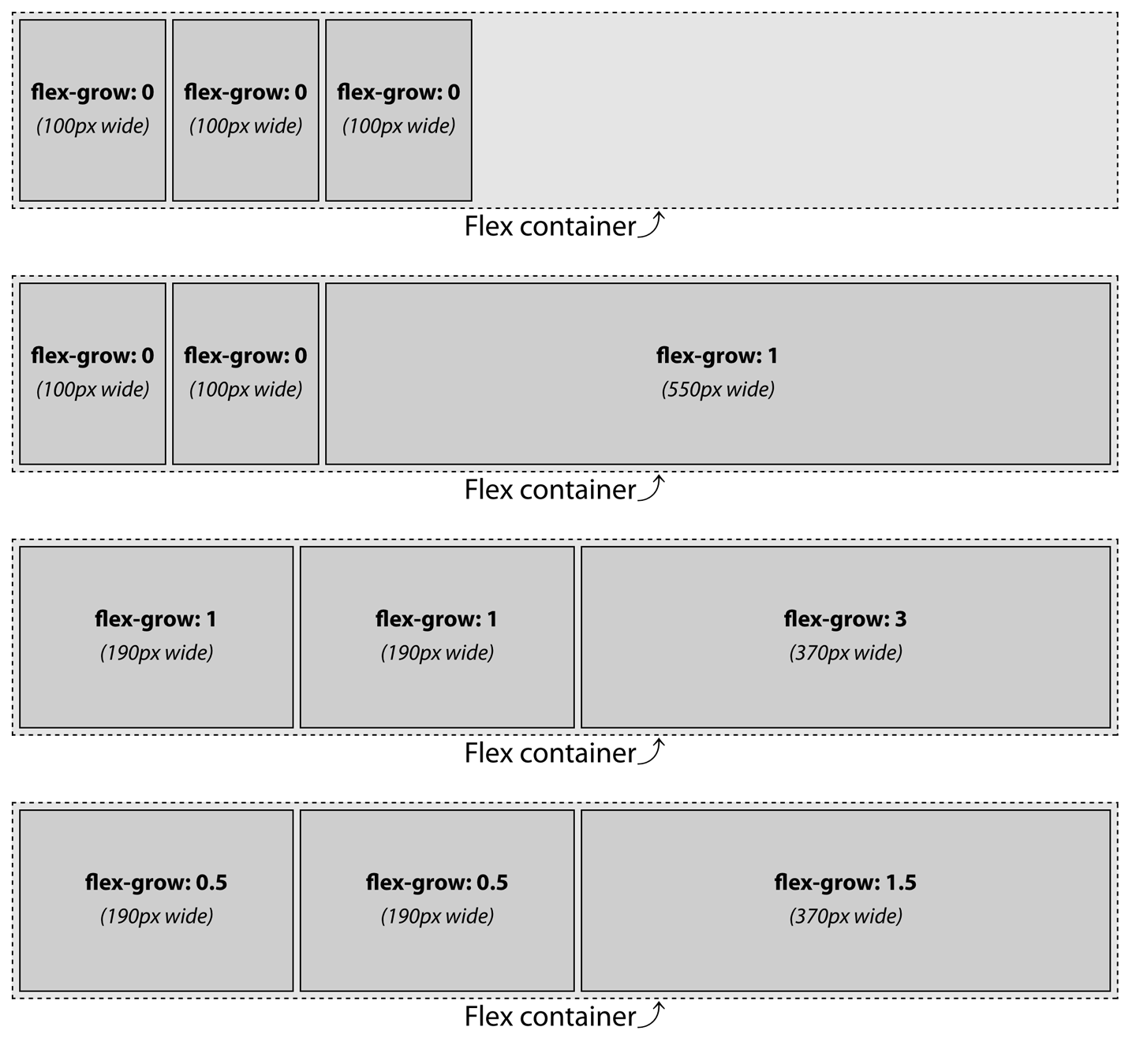
- 如果
flex 项没有设置width或flex-basis,则flex-basis默认为auto,这意味着每个flex-basis是其非换行内容的宽度。即如果flex 项没有设置宽度,此时flex-basis将成为该宽度。 - 如果
flex-basis被设置为0%或者默认值auto,且增长因子为 0 时,非增长的flex 项的主轴长度将收缩到内容允许的最小长度(即 最宽字母序列的宽度),或更小。 - 如果所有的
flex 项都允许增长,并且每个flex 项的flex-basis都时0%,那么所有的空间,而不仅仅时额外空间,将根据增长因子按比例分配。
flex-shrink
如果
flex 项中包含一个固定像素(300px)图像,则该flex 项不会收缩。flex 项是与收缩因子和其宽度成比例的收缩的。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10ShrinkPercent(收缩百分比) = NegativeSpace(缺少空间) / ((Width1 * ShrinkF1) + ... + (WidthN * ShrinkFN))
// 例如 缺少空间:250px, flex项宽度: 250px 500px 250px; flex-shrink: 1 1 3
收缩百分比 = 250px / ((250px * 1) + (500px *1 ) + (250px * 3))
= 250px / 1500px
= 0.1666666667 (16.67%)
item1 = 250px - (250px * 16.67% * 1) = 208.33px
item2 = 500px - (500px * 16.67% * 1) = 416.67px
item3 = 250px - (250px * 17.67% * 3) = 125px
flex-basis
1 | Value: content|[<length> | <percentage>] |
- 当没有其他属性(如:
width,min-width)设置主轴上flex 项,flex-basis:auto或flex: 0 1 auto,则flex 项的宽度会尽可能的去适应其内容 flex 项上既设置了width,又设置了flex-basis,则flex-basis胜出。flex 项上既设置了min-width,又设置了flex-basis,则min-width胜出。flex-basis百分比数,是根据fkex 容器的主轴尺寸大小计算的。flex-basis:auto,“可用”空间是基于flex 项的 内容大小;flex-basis:0,那么”可用”空间就是整个flex 容器主轴的大小。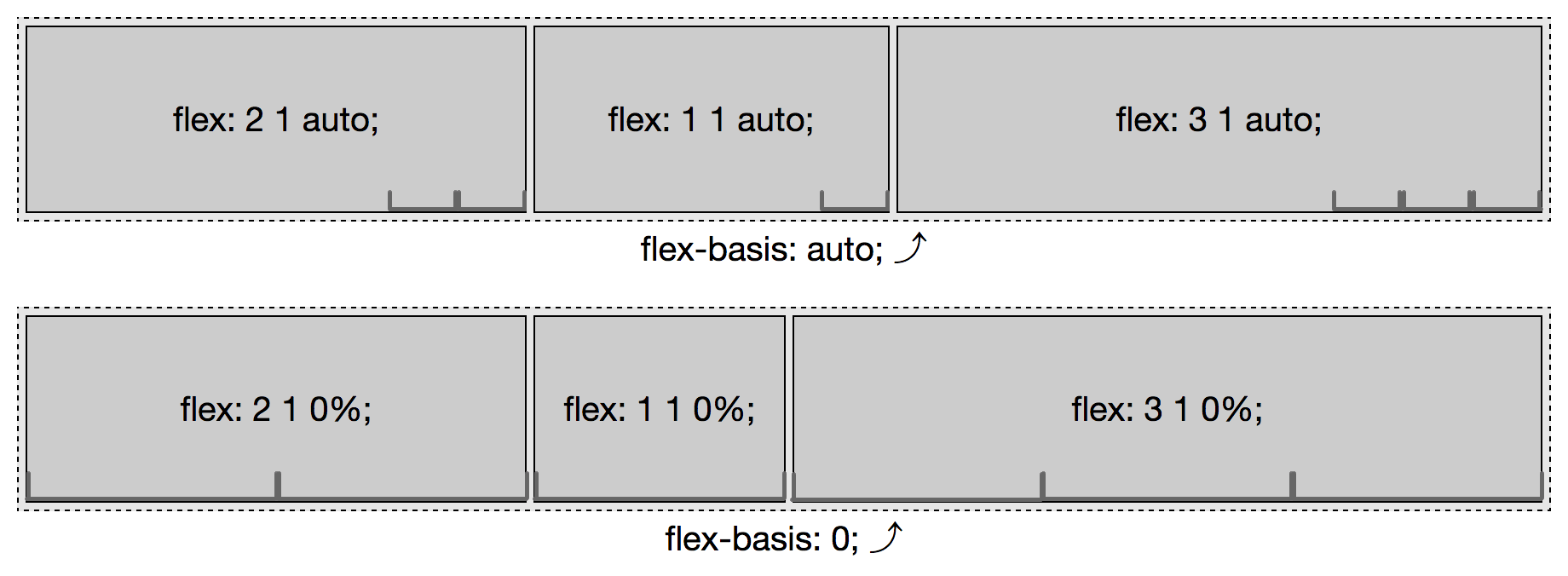
flex 简写(Flex Shorthand)
切记,总是要使用flex简写,它接受 3 个全局属性值,initial,auto,none,和一个数值。
flex:initial等同于flex: 0 1 auto;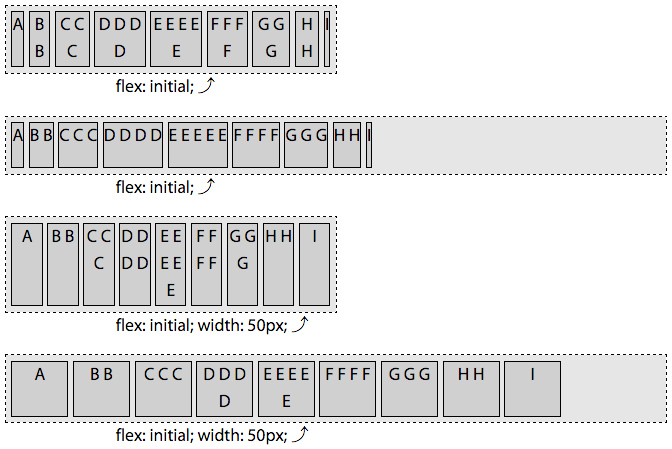
flex:auto等同于flex: 1 1 auto;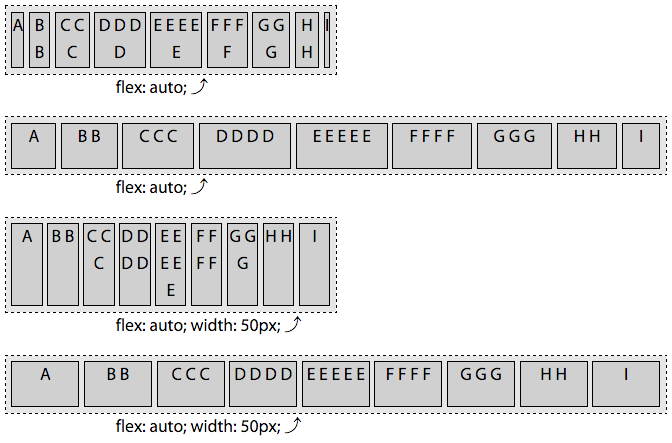
flex:none等同于flex: 0 0 auto;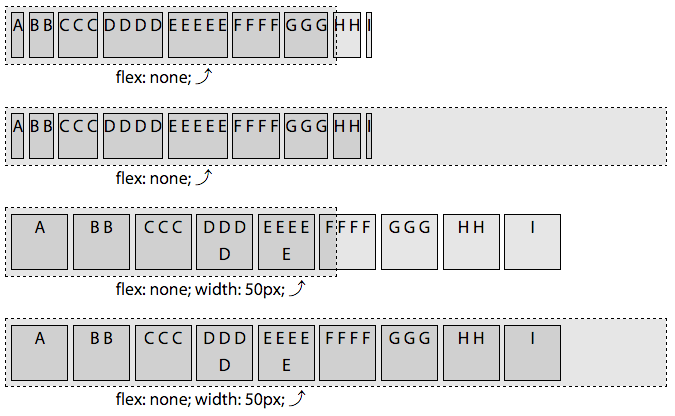
flex:<number>,flex:3等同于flex:3 0 0;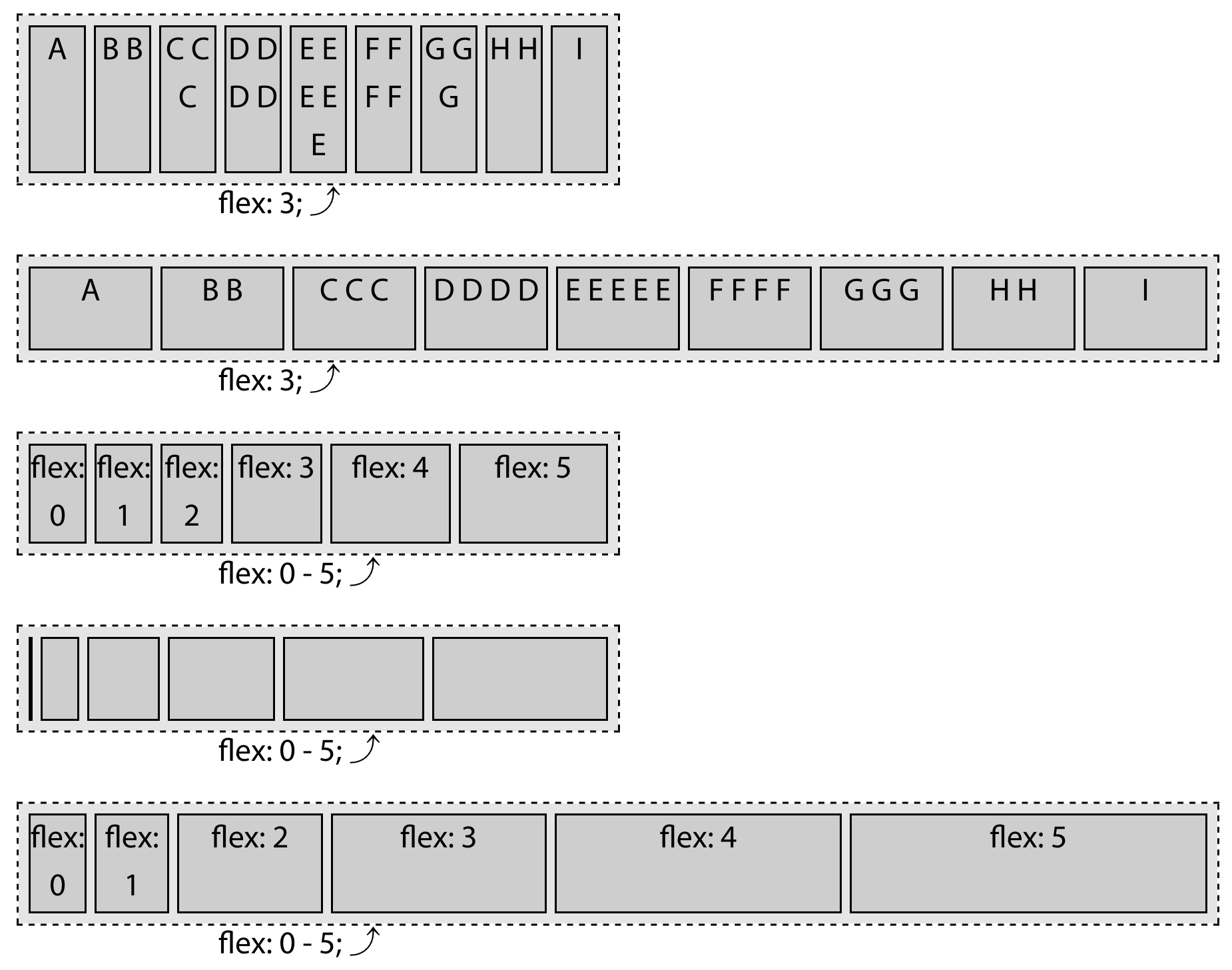
flex 项 顺序
默认,所有的
flex 项的顺序都是 0.order属性指定flex 项所属的序号组,负值的flex 项出现在默认值为 0 的项之前,正值的flex 项出现在之后。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12ul {
display: inline-flex;
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
}
li:nth-of-type(3n-1) {
order: 3;
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.2);
}
li:nth-of-type(3n+1) {
order: -1;
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,0.4);
}- item 2,5,8,11 的顺序组是 3
- item 1,4,7,10 的顺序组是-1
- item 3,6,9,12 的 顺序组是 0
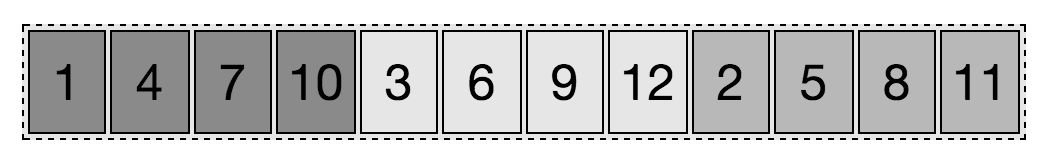
按
tab 键是按照源代码的顺序,而不是按布局的顺序。order属性仅改变布局的顺序,源代码顺序不变。


