节流和防抖是的两种广泛使用的技术,用于提高在一段时间内重复执行的代码的性能。这两个函数通常用于处理这样的情况:用户正在导致事件处理程序重复触发,而我们希望降低底层函数调用的速度。比如,滚动处理程序,键盘事件、甚至只是快速的点击一个按钮。
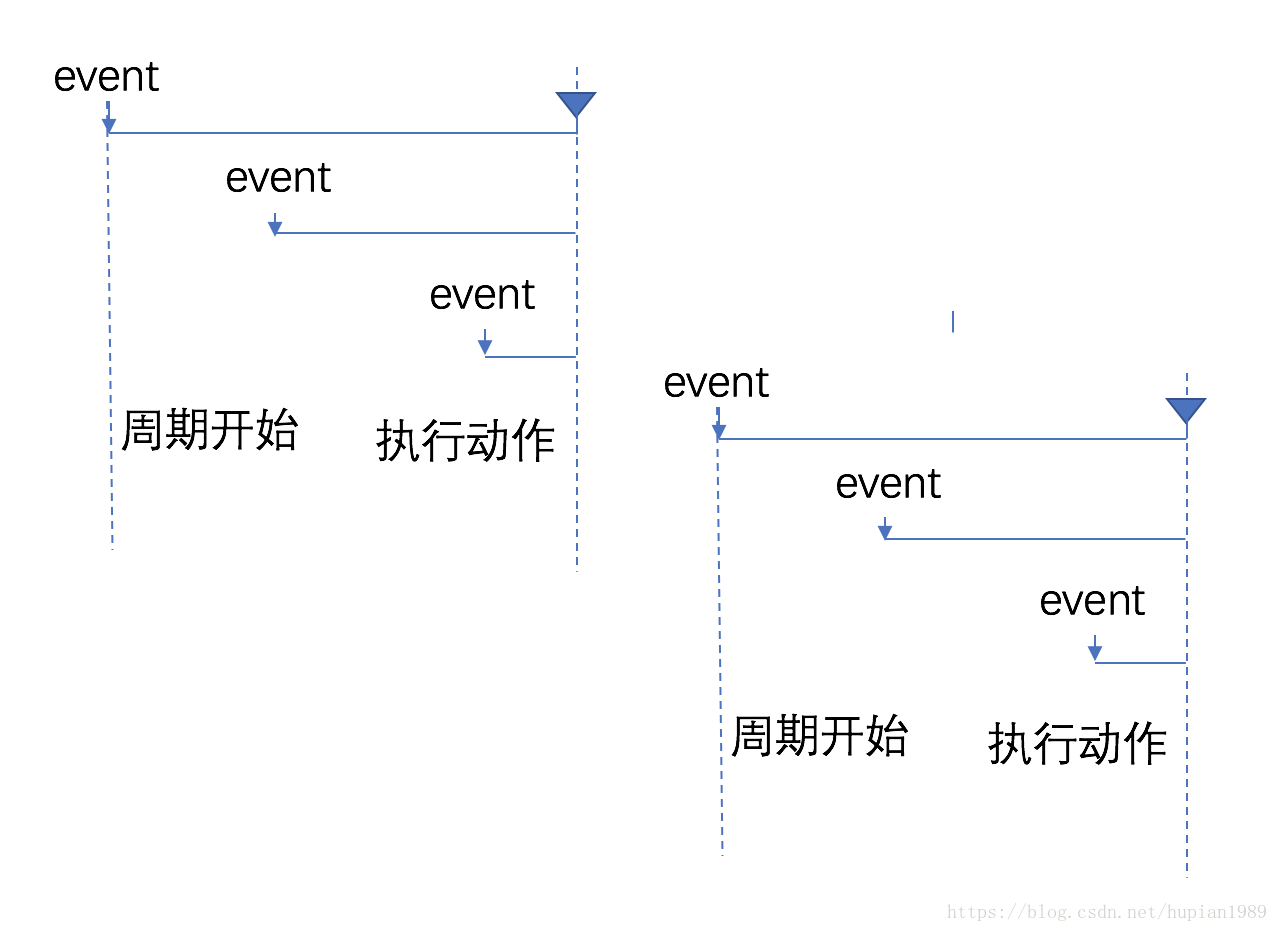
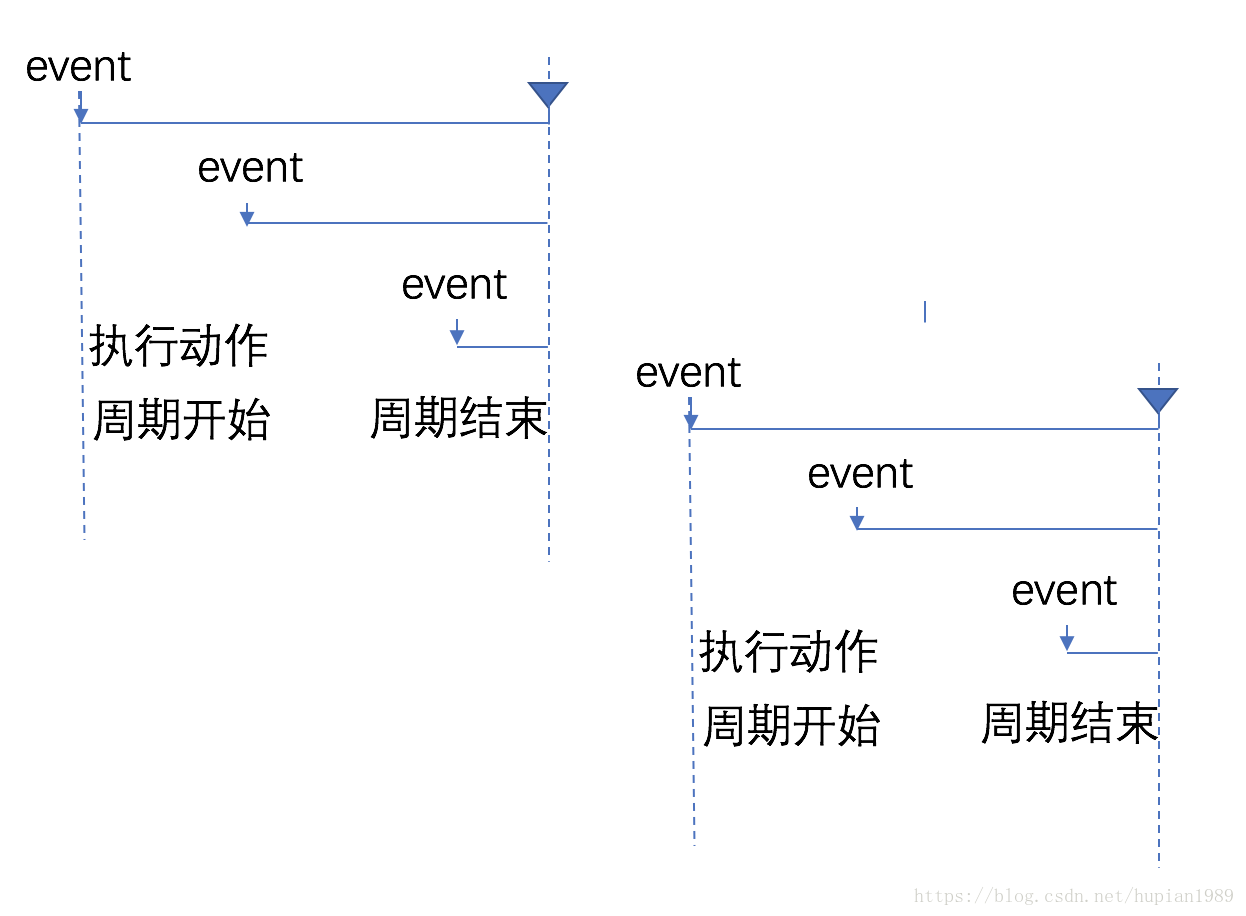
节流(Throttle) 函数在指定的时间段内最多执行一次。固定周期内,函数只执行一次,若在该周期内又调用该函数,则不执行。周期结束后,又有调用,则开始新的周期。
简单实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 function throttle (func,timeout ) { let ready = true ; return (...args ) => { if (!ready) { return ; } ready = false ; func (...args); setTimeout (() => { ready = true ; }, timeout); } }
节流策略有 2 种:
周期结束后 执行动作 (函数在每个等待时延的结束被调用,trailing:true)
执行动作后 开始周期 (函数在每个等待时延的开始被调用, leading: true)
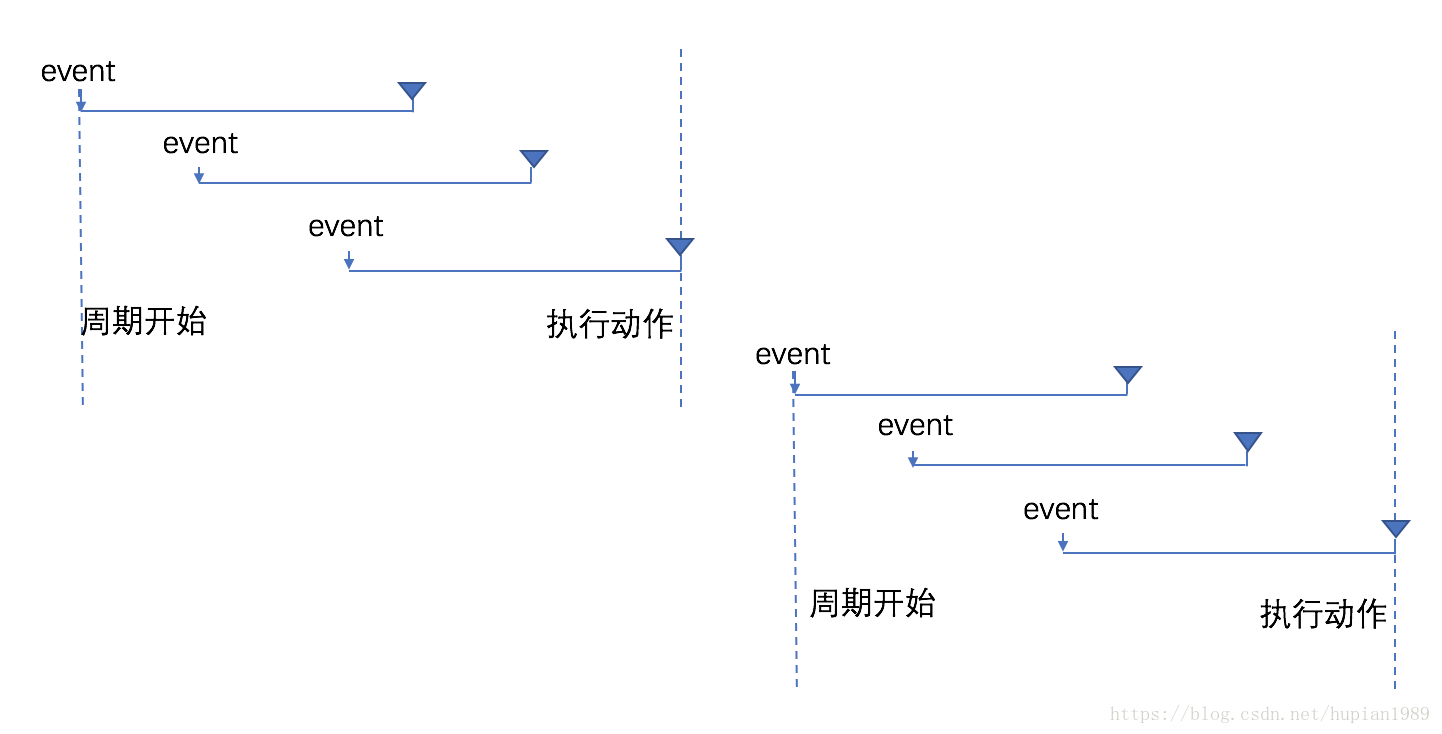
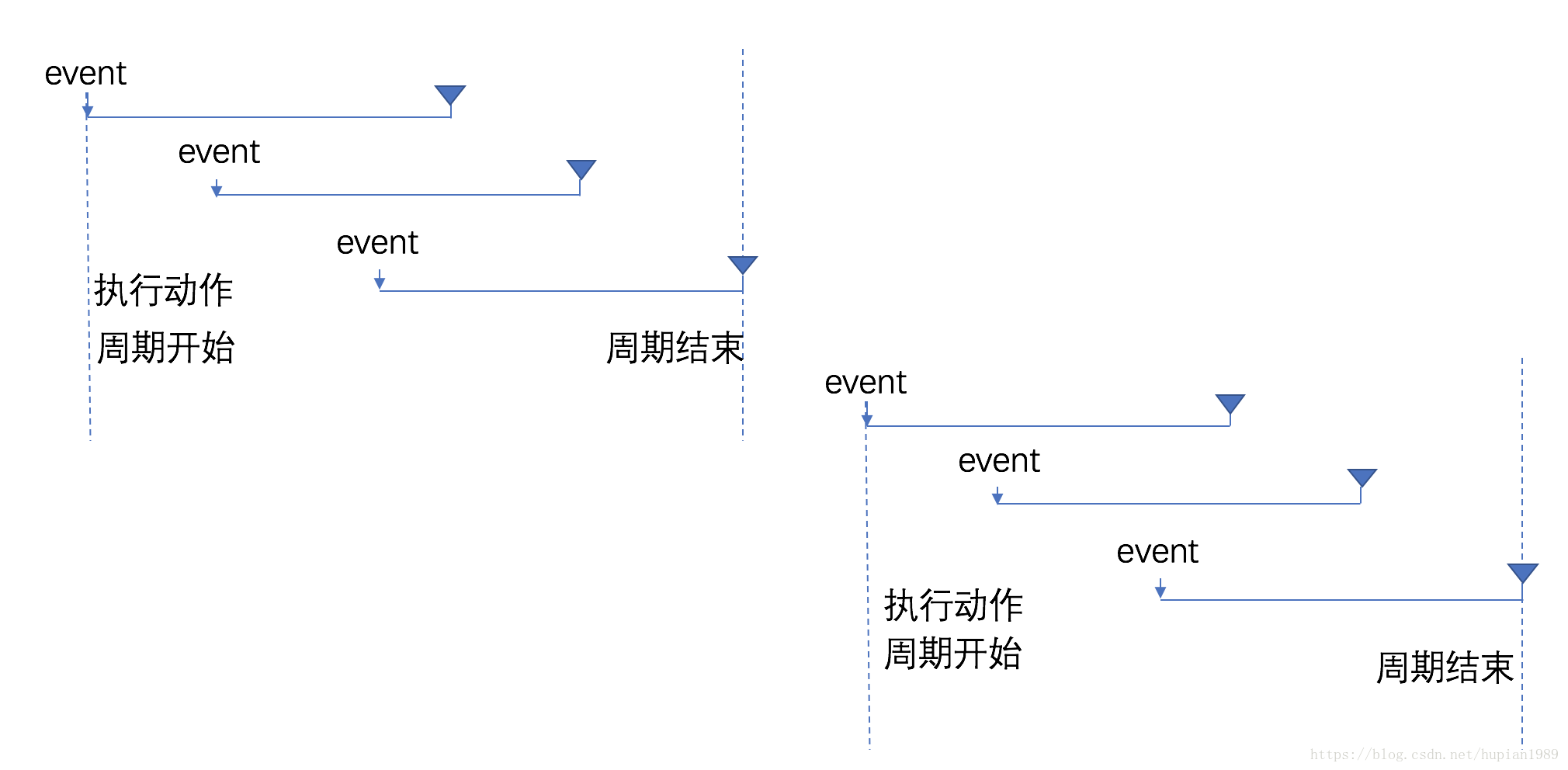
防抖(Debounce) 函数在停止调用以后的指定时间段后执行。当调用函数 n 秒后,才会执行,若在这 n 秒内又调用了该函数,则取消前一次计时并重新计算执行的时间。
简单实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 function debounce (func,timeout ) { let timer; return (...args ) => { clearTimeout (timer); timer = setTimeout (() => { func (...args); },timeout); } }
防抖策略也有 2 种:
周期结束后 执行动作 (函数在每个等待时延的结束被调用,trailing:true)
执行动作后 开始周期 (函数在每个等待时延的开始被调用, leading: true)
lodash 内 _throttle 与 _debounce _debounce(func,[wait=0],[options={}]) 创建一个 debounced(防抖动)函数,该函数会从上一次被调用后,延迟 wait 毫秒后调用 func 方法。 debounced(防抖动)函数提供一个 cancel 方法取消延迟的函数调用以及 flush 方法立即调用。 可以提供一个 options(选项) 对象决定如何调用 func 方法,options.leading 与|或 options.trailing 决定延迟前后如何触发(是 先调用后等待 还是 先等待后调用)。 func 调用时会传入最后一次提供给 debounced(防抖动)函数 的参数。 后续调用的 debounced(防抖动)函数返回是最后一次 func 调用的结果。
注意:
如果 leading 和 trailing 选项为 true,则 func 在 wait 期多次调用防抖方法
如果 wait 为 0 并且 leading 为 false, func 调用将被推迟到下一个点,类似 setTimeout 为 0 的超时
options参数中定义了一些选项:主要有以下 3 个:
leading , 函数在每个等待时延的开始被调用,默认值:false
trailing , 函数在每个等待的结束时被调用,默认值:true
maxwait , 最大的等待时间,因为 _debounce 的函数调用时间不满足条件,可能永远都无法触发,增加该配置,保证了大于一段时间后一定能执行一次函数。
_debounce 还有cancel方法,用于取消防抖调用
_throttle(func,[wait=0],[options{}]) 创建一个节流函数,在 wait 秒内最多执行 func 一次的函数。 该函数提供一个 cancel 方法取消延迟的函数调用以及 flush 方法立即调用。 可以提供一个 options 对象决定如何调用 func 方法, options.leading 与|或 options.trailing 决定 wait 前后如何触发。 func 会传入最后一次传入的参数给这个函数。 随后调用的函数返回是最后一次 func 调用的结果
注意:
如果 leading 和 trailing 都为 true 则 func 在 wait 期间会被多次调用
如果 wait 为 0,并且 leading 为 false,func 调用将被推迟到下一个点,类似 setTimeout 为 0 的超时
_throttle 其实就是设置了 maxwait 的 debounce. optinons参数同样定义了leading和trailing选项,与 debounce 含义相同。
用例: _debounce 源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 function debounce (func, wait, options ) { let lastArgs; let lastThis; let maxWait; let result; let timerId; let lastCallTime; let lastInvokeTime = 0 ; let leading = false ; let maxing = false ; let trailing = true ; if (typeof func !== "function" ) { throw new TypeError ("Expected a function" ); } wait = +wait || 0 ; if (isObject (options)) { leading = !!options.leading ; maxing = "maxWait" in options; maxWait = maxing ? Math .max (+options.maxWait || 0 , wait) : maxWait; trailing = "trailing" in options ? !!options.trailing : trailing; } function isObject (value ) { const type = typeof value; return value != null && (type === "object" || type === "function" ); } function invokeFunc (time ) { let args = lastThis; let thisArg = lastThis; lastAr = lastThis = undefined ; lastInvokeTime = time; result = func.apply (thisArg, args); return result; } function shouldInvoke (time ) { const timeSinceLastCall = time - lastCallTime; const timeSinceLastInvoke = time - lastInvokeTime; return ( lastCallTime === undefined || timeSinceLastCall >= wait || timeSinceLastCall < 0 || (maxing && timeSinceLastInvoke >= maxWait) ); } function leadingEdge (time ) { lastInvokeTime = time; timerId = setTimeout (timerExpired, wait); return leading ? invokeFunc (time) : result; } function trailingEdge (time ) { timerId = undefined ; if (trailing && lastArgs) { return invokeFunc (time); } lastArgs = lastThis = undefined ; return result; } function timerExpired ( let time = Date .now (); if (shouldInvoke (time)) { return trailingEdge (time); } timerId = setTimeout (timerExpired, remainingWait (time)); } function remainingWait (time ) { let timeSinceLastCall = time - lastCallTime; let timeSinceLastInvoke = time - lastInvokeTime; let timeWaiting = wait - timeSinceLastCall; return maxing ? Math .min (timeWaiting, maxWait - timeSinceLastInvoke) : timeWaiting; } function debounced (...args ) { const time = Date .now (); const isInvoking = shouldInvoke (time); lastArgs = args; lastThis = this ; lastCallTime = time; if (isInvoking) { if (timerId === undefined ) { return leadingEdge (lastCallTime); } if (maxing) { timerId = setTimeout (timerExpired, wait); return invokeFunc (lastCallTime); } } if (timerId === undefined ) { timerId = setTimeout (timerExpired, wait); } return result; } function flush ( return timerId === undefined ? result : trailingEdge (Date .now ()); } function cancel ( if (timerId !== undefined ) { clearTimeout (timerId); } lastInvokeTime = 0 ; lastArgs = lastCallTime = lastThis = timerId = undefined ; } debounced.cancel = cancel; debounced.flush = flush; return debounced; }
_throttle 源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 * * jQuery (window ).on ('scroll' , throttle (updatePosition, 100 )) * * * const throttled = throttle (renewToken, 300000 , { 'trailing' : false }) * jQuery (element).on ('click' , throttled) * * * jQuery (window ).on ('popstate' , throttled.cancel ) * function throttle (func, wait, options ) { let leading = true ; let trailing = true ; if (typeof func !== "function" ) { throw new TypeError ("Expected a function" ); } if (isObject (options)) { leading = "leading" in options ? !!options.leading : leading; trailing = "trailing" in options ? !!options.trailing : trailing; } return debounce (func, wait, { leading, trailing, maxWait : wait }); }